Interstellar Comet | NASA's Shocking Find!
Here’s the thing: when NASA releases images of an interstellar comet , it’s not just a pretty picture. It’s a story unfolding light-years away, a cosmic mystery begging to be understood. Comet 3I/ATLAS, that icy wanderer from another solar system, has once again graced our telescopes, and the resulting images are more than just visually stunning – they’re packed with clues about the very formation of planetary systems beyond our own. So, let’s dive into why these images are so darn important, and what they tell us about the universe we live in.
Why This Interstellar Comet Matters: Beyond the Pretty Pictures
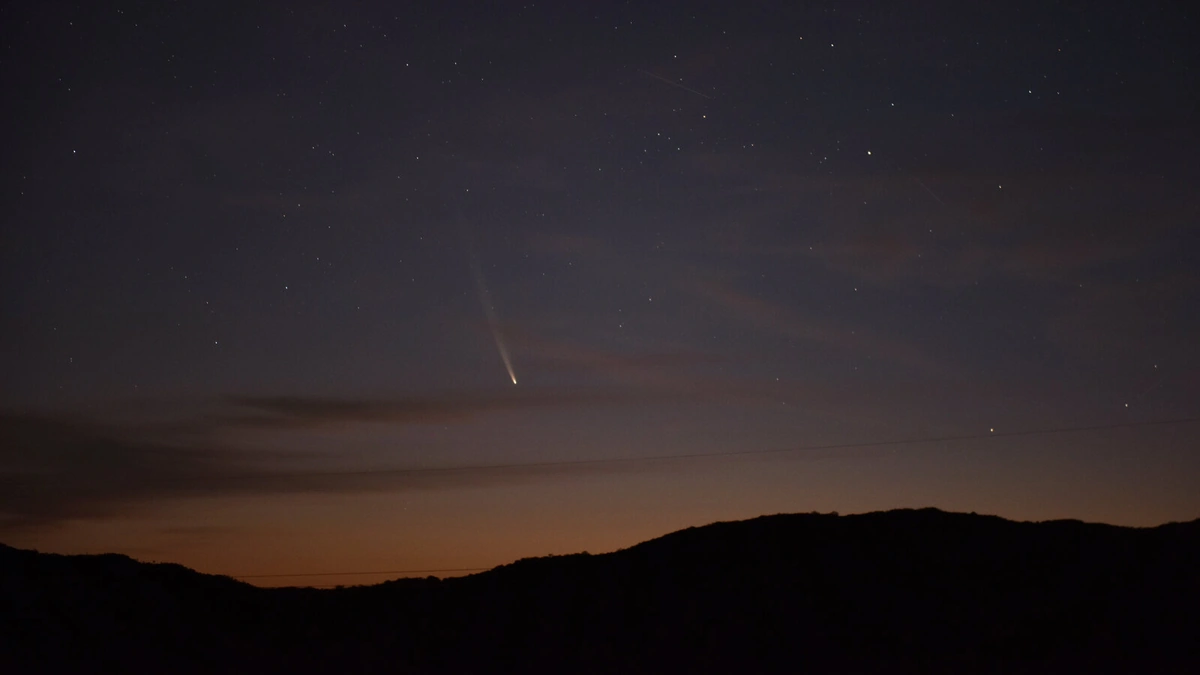

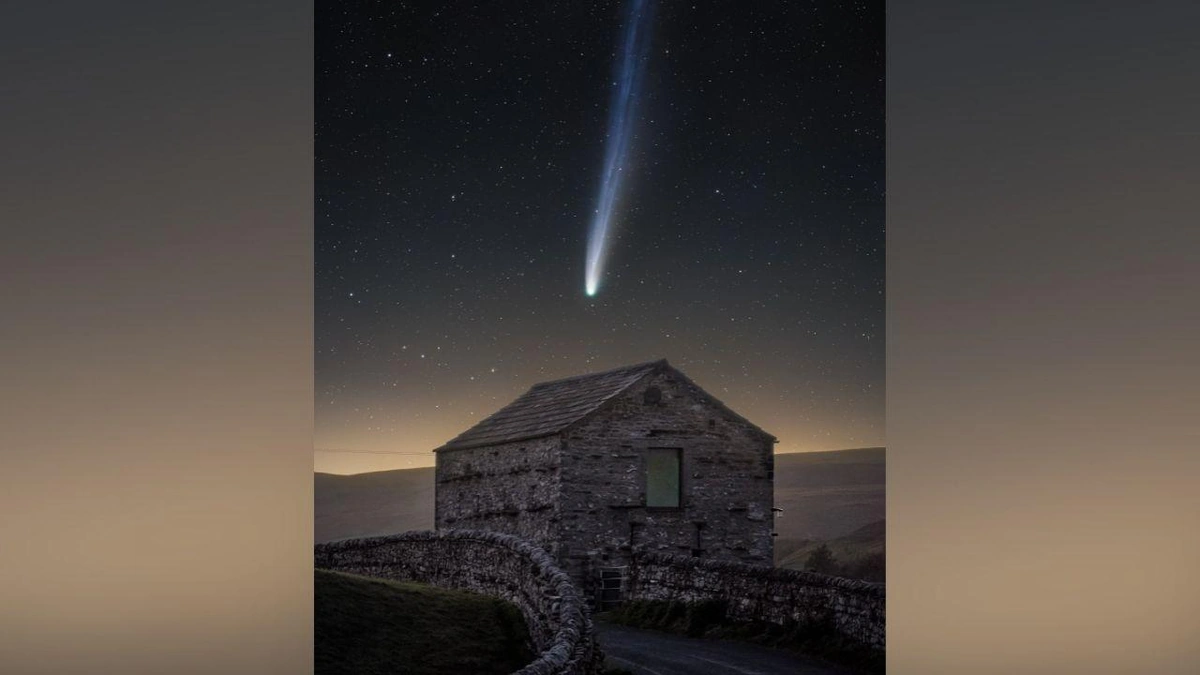
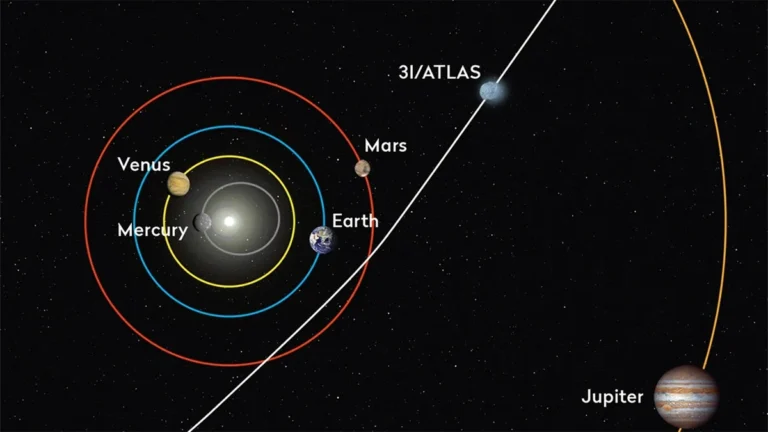
We’ve all seen those dazzling pictures of comets – streaks of light against the inky blackness. But Comet 3I/ATLAS is different. It’s an interstellar object, meaning it didn’t originate in our solar system. It’s a traveler from another star, making a fleeting visit before continuing its journey through the galaxy. The sheer rarity of these interstellar visitors is what makes them so valuable to scientists. They are messengers from alien star systems, potentially carrying information about the building blocks of planets elsewhere in the Milky Way. What fascinates me is that, as theia moon origin discovered , we learn more about our universe.
But, it’s not just about the origin. Studying Comet 3I/ATLAS allows us to test our existing models of how comets evolve as they approach a star. According to NASA , the comet’s composition and behavior can reveal details about the environment it formed in and the processes it has undergone during its long journey through interstellar space. The data gathered can then be compared with what we know about comets in our solar system, providing a broader understanding of cometary activity and its relationship to the surrounding stellar environment. It’s like comparing notes with other civilizations, only on a cosmic scale!
Decoding the Images | What Can We Learn?
So, what exactly can we learn from these images? Firstly, the images provide data about the comet’s size and shape. Measuring the comet’s nucleus (its solid, icy core) and the surrounding coma (the cloud of gas and dust that forms as the comet heats up) helps scientists estimate its mass and density. The shape of the coma and any visible jets of gas and dust can reveal information about the comet’s internal structure and how it interacts with the solar wind.
Secondly, the images can tell us about the comet’s composition. By analyzing the light reflected from the comet , scientists can identify the different molecules present in its coma and tail. This can reveal the types of ice and dust that make up the comet, providing clues about the conditions in its parent star system. For example, the presence of certain organic molecules could suggest that the comet formed in a region where life might be possible.
I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized how much meticulous detail goes into the image processing. Experts filter the images and use advanced algorithms to remove noise and enhance subtle features of the comet that would otherwise be imperceptible.
The Challenges of Interstellar Observation
Observing interstellar objects isn’t easy, let’s be honest. They’re often faint and fast-moving, making them difficult to track. And because they’re only passing through our solar system, we have a limited window of opportunity to study them. This is where powerful telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories come into play. Their ability to collect light and resolve fine details is crucial for capturing high-quality images and data.
The other major challenge? Predicting where these interstellar visitors will appear. Discovering the missing planet . While we can track their trajectories once they’re detected, spotting them in the first place requires a combination of luck and systematic sky surveys. As technology improves, we can expect to find more of these cosmic travelers. What fascinates me is how a better understanding of galactic orbital dynamics helps astronomers predict the arrival of future interstellar objects.
Comet 3I/ATLAS was discovered by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey, which scans the sky for potentially hazardous asteroids. Its interstellar nature was confirmed by its highly eccentric orbit, which indicated that it was not bound to our sun. So, it’s a guest, not a resident!
What This Means for Understanding Our Place in the Universe
Ultimately, studying interstellar objects like comet 3I/ATLAS helps us understand our place in the universe. It allows us to test our theories about planet formation and the distribution of matter in the galaxy. It gives us a glimpse of what other star systems might be like. And it reminds us that our solar system is not an isolated island, but part of a vast, interconnected cosmic ocean. As per , this perspective underscores the need to continue exploring and studying the universe around us.
The one thing you absolutely must remember is that each new discovery builds upon previous research. Each new image adds a piece to the puzzle. It is this collaborative, incremental journey of discovery that makes astronomy so rewarding. Here’s the thing: astronomy compels people to look up and wonder, fostering a sense of curiosity and awe.
Looking Ahead | Future Interstellar Explorations
What does the future hold for interstellar exploration? With new telescopes and spacecraft on the horizon, we can expect to learn even more about these cosmic visitors. The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, currently under construction in Chile, will be able to scan the sky much faster and deeper than existing telescopes, potentially discovering many more interstellar objects. And future missions could even attempt to intercept and sample these objects directly, bringing samples of alien material back to Earth for analysis. The possibilities are endless, but more importantly, the future of interstellar explorations is bright.
FAQ About Interstellar Comets
What exactly is an interstellar comet?
It’s a comet that originated outside our solar system, making a temporary visit.
How do scientists know it’s not from our solar system?
Its orbit is highly eccentric, indicating it’s not gravitationally bound to our sun.
What if I want to see it myself?
Unfortunately, Comet 3I/ATLAS is no longer visible to the naked eye, and requires powerful telescopes to observe.
Why are interstellar comets so important to study?
They provide clues about planet formation and the building blocks of other star systems.
Could an interstellar comet pose a threat to Earth?
While theoretically possible, the chances of an interstellar comet directly impacting Earth are extremely low.
Where can I find the latest updates on Comet 3I/ATLAS?
Check NASA’s official website for the most current information and images.
So, the next time you see a picture of a comet , remember that it’s not just a beautiful image, it’s a story of cosmic travel, stellar origins, and our ongoing quest to understand the universe. And that, my friend, is a story worth following.