Saturn's Rings Vanishing?! Here's Why It Matters
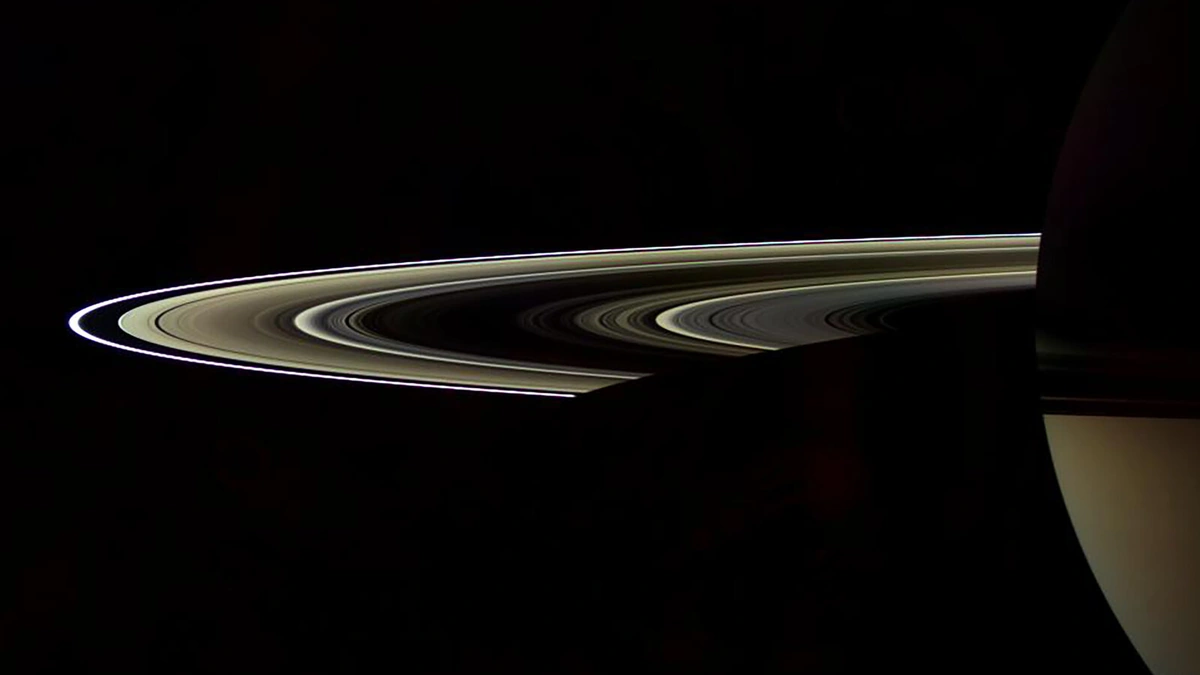
Saturn’s rings. Just hearing the words conjures images of cosmic beauty, doesn’t it? Those iconic rings, shimmering in the sunlight, have captivated stargazers for centuries. But here’s the thing: they aren’t going to be around forever. And, honestly, that realization hit me harder than I expected. It’s not just some distant astronomical event; it’s a reminder that even the most breathtaking sights in the universe are temporary. Let’s be honest, the thought of Saturn’s rings vanishing is kind of a bummer. So, why are they disappearing, and what does it even mean for us here on Earth? Let’s dive in.
Why Saturn’s Rings Are Fading Away
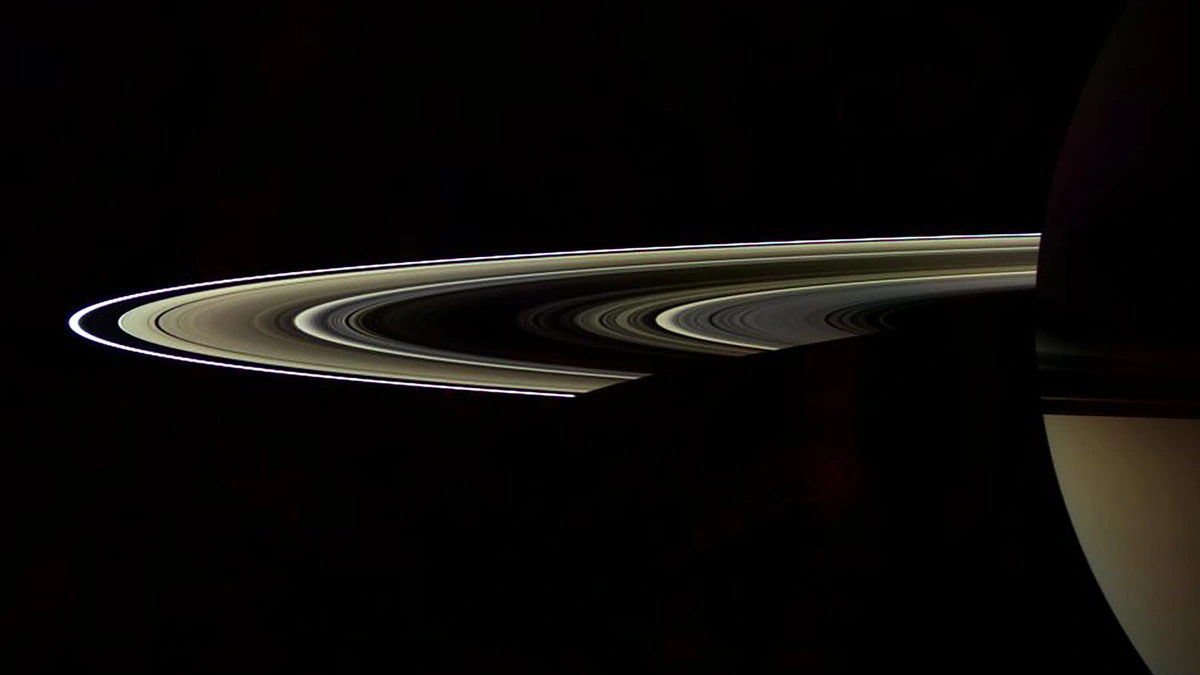

Okay, so here’s the deal. The rings aren’t vanishing in a puff of smoke overnight (thank goodness!). It’s a slow, steady process – a cosmic erosion, if you will. The primary culprit? A phenomenon scientists are calling “ring rain”. Imagine tiny, icy particles that make up the rings being pulled down onto Saturn by gravity and the planet’s magnetic field. It’s like a gentle, but constant, snowfall onto the planet, but instead of snow, it’s ring material. The rate at which the rings are losing material is quite astonishing. Scientists estimate that the rings could be gone in a mere 300 million years. Okay, 300 million years is a long time for us humans, but in cosmic terms, it’s practically a blink of an eye.
But, what fascinates me is the composition of these rings. They aren’t solid structures, but rather collections of ice particles, dust, and debris, ranging in size from tiny grains to house-sized chunks. These particles are constantly colliding and interacting, creating a dynamic and ever-changing environment. And this constant activity contributes to the “ring rain” effect. The exact age of the rings is still debated, but evidence suggests they might be relatively young, perhaps only a few hundred million years old. This means we’re incredibly lucky to be alive at a time when they’re still around to observe!
The Science Behind Ring Rain
So, how does this “ring rain” actually work? It all comes down to the interaction between the ice particles in the rings, Saturn’s gravity, and its magnetic field. The ice particles become electrically charged, and this charge interacts with Saturn’s magnetic field. This interaction causes the particles to be drawn along the magnetic field lines towards the planet’s atmosphere. As these particles enter the atmosphere, they vaporize, creating a sort of icy rain. The process is surprisingly complex, involving various factors like the angle of the sun, the composition of the rings, and the strength of Saturn’s magnetic field. Scientists are still working to fully understand all the intricacies of the ring rain phenomenon .
What’s really cool is that this process isn’t just theoretical. Scientists have actually observed the effects of ring rain using telescopes and spacecraft. Data from the Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn for over a decade, provided invaluable insights into the rate and distribution of ring rain. These observations confirmed that the rings are indeed disappearing and that the process is happening much faster than previously thought. Sleep pattern may get disturbed if such thing keep wondering in your mind.
The Fate of Saturn’s Iconic Feature
Okay, so what happens when the rings are completely gone? Well, Saturn will still be a magnificent planet, of course. It will still have its beautiful atmosphere, its intriguing moons, and its powerful magnetic field. But it will lose that iconic feature that makes it so recognizable and so captivating. It will become just another gas giant in our solar system. This raises some interesting questions about the role of rings in planetary systems. Do all gas giants have rings at some point in their history? Are rings a temporary phenomenon? And what can the study of Saturn’s ring system tell us about the formation and evolution of our solar system?
What I initially thought was a simple explanation of a natural phenomenon turned out to be a rabbit hole of fascinating science and profound implications. The disappearance of Saturn’s rings isn’t just about losing a beautiful sight; it’s about understanding the dynamic processes that shape our universe. But, let’s be honest, the visuals will be missed. We have been lucky enough to witness such a beautiful and rare phenomenon. Beauty tips cannot replace such experience of observing Saturn’s ring.
What We Can Learn from Saturn’s Rings
The study of Saturn’s rings provides valuable insights into a range of scientific fields, from planetary science to astrophysics. By studying the composition, structure, and dynamics of the rings, scientists can learn more about the formation and evolution of planetary systems. The rings act as a sort of cosmic laboratory, allowing us to study the interactions between gravity, magnetism, and radiation in a unique environment. The findings could even provide clues about how our own solar system formed and how it might evolve in the future. This is important to note.
The rings also offer a unique opportunity to study the effects of micrometeoroid bombardment. The constant stream of tiny meteoroids that impact the rings provides a natural experiment for understanding how dust and debris behave in space. By analyzing the composition of the ring particles, scientists can learn more about the types of materials that are present in the outer solar system. And that’s not all.
The Broader Implications for Space Exploration
The eventual disappearance of Saturn’s rings should give us pause about how important it is to continue space exploration. The more we learn about our solar system and beyond, the better we can prepare for the future. The loss of the rings is an important reminder that the universe is constantly changing and that we need to keep pushing the boundaries of our knowledge. The future of space exploration depends on it. We need to discover new things.
Furthermore, understanding the forces at play in Saturn’s system, including the planet’s magnetic field and gravitational pull, is crucial for planning future missions to other planets. It gives us an insight on how celestial bodies affect each other and make it possible to be more exact in the exploration of the universe.
FAQ About Saturn’s Rings
How long until Saturn’s rings disappear?
Scientists estimate that the rings could be gone in approximately 300 million years.
What is “ring rain”?
“Ring rain” is the process where icy particles from the rings are pulled down onto Saturn by gravity and the planet’s magnetic field.
Are Saturn’s rings solid?
No, the rings are composed of countless ice particles, dust, and debris.
Can we still see Saturn’s rings today?
Yes, Saturn’s rings are still visible through telescopes.
What happens when the rings are gone?
Saturn will lose its iconic feature, but it will still be a magnificent planet.
Why are scientists studying Saturn’s rings?
The study of Saturn’s rings provides insights into planetary science, astrophysics, and the formation of planetary systems.
So, there you have it. The disappearance of Saturn’s rings is a slow, inevitable process, but one that offers a unique opportunity to learn more about the universe we live in. It’s a reminder that even the most beautiful and awe-inspiring sights are temporary, and that we should appreciate them while they last. What a thought, huh?