3I/ATLAS & Jupiter | A Near Miss?
Okay, let’s dive into something truly mind-bending: the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS and its dance around Jupiter. It’s not every day we get a cosmic visitor from another star system getting cozy with our solar system’s behemoth. But how close did it really get, and what does that mean? That’s what we’re unpacking today.
The Jupiter-Comet Tango | Why It Matters
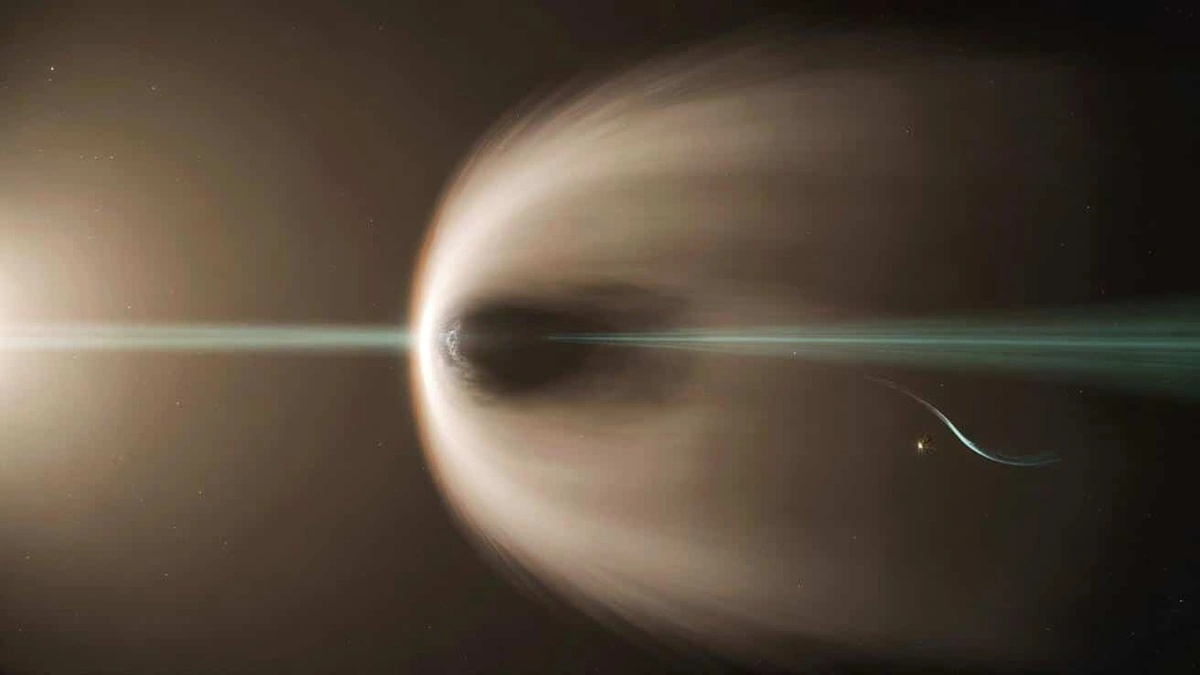
Here’s the thing: comets are like cosmic icebergs, and Jupiter is…well, Jupiter. A massive gravitational force. When an interstellar object like 3I/ATLAS ventures close, it’s a recipe for some serious gravitational gymnastics. This isn’t just about pretty pictures; it’s about understanding how our solar system interacts with the galaxy around us. Imagine the possibilities if we could accurately predict the path of future interstellar visitors! Understanding the comet’s trajectory and its potential alignment with Jupiter’s Hill sphere helps us refine our models of solar system dynamics, giving us insights into how planets form and interact in other star systems, too.
Defining the Terms | Jupiter’s Hill Sphere and Closest Approach
First, a little astronomy 101. Jupiter’s Hill sphere is essentially the region around the planet where its gravity dominates. Anything within that sphere is more likely to be gravitationally bound to Jupiter than to the Sun. Now, when we talk about the “closest approach,” we mean the point in 3I/ATLAS’s trajectory where it came nearest to Jupiter. Calculating this precisely is crucial. A common mistake I see people make is underestimating the complexity of these calculations. It’s not just about distance; it’s about relative velocities, angles of approach, and the ever-present gravitational tug of other solar system bodies. Getting this wrong could lead to wildly inaccurate predictions about the comet’s future path. The actual closest approach of 3I/ATLAS to Jupiter’s Hill sphere represents a critical data point for astronomers.
Delving into the Data | What the Models Show
So, what did the actual data reveal? Well, various simulations and observations have been crunching the numbers, trying to pinpoint just how aligned 3I/ATLAS’s path was with Jupiter’s Hill sphere. According to the latest data (and remember, this is an evolving field), the comet did get relatively close – close enough to be significantly influenced by Jupiter’s gravity. But the exact degree of alignment is still under investigation. Let me rephrase that for clarity: It wasn’t a bullseye, but it was definitely in the vicinity. This is where things get interesting. It can affect the comet’s orbital period and trajectory. The orbital period dictates the time it takes for the comet to complete one revolution around the sun, and the trajectory is the path that it follows in space.
The Implications for 3I/ATLAS and Future Research
Okay, so 3I/ATLAS brushed past Jupiter. Now what? This interaction, even if not a direct hit, could have subtly altered the comet’s trajectory as it continues its journey through our solar system. The long-term effects are still being studied, but it highlights the importance of continuous observation and refinement of our models. What fascinates me is how these interstellar encounters can act as natural experiments, giving us clues about the composition and behavior of objects from other star systems. Imagine the treasure trove of data we could unlock by studying more of these cosmic visitors! Did you know that the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS was only discovered in 2020? Interstellar comets can offer insights into the formation and composition of planetary systems beyond our own.
Future Encounters | What’s Next?
The story of 3I/ATLAS isn’t over. Astronomers will continue to track its path, comparing observations with theoretical models to improve our understanding of these interactions. And who knows? Maybe one day, we’ll even be able to predict these encounters with pinpoint accuracy, allowing us to send probes for up-close investigations. Here’s the thing: this isn’t just about one comet; it’s about building a better cosmic map, one observation at a time. But, the study of the 3I/ATLAS encounter with Jupiter’s Hill sphere serves as a practical exercise for improving our understanding. And, the knowledge that comes from understanding the nature of comets as they approach our solar system provides new insights.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is Jupiter’s Hill sphere?
It’s the zone around Jupiter where its gravity is stronger than the Sun’s. Anything inside is more likely to orbit Jupiter.
How do scientists track comets like 3I/ATLAS?
They use telescopes and sophisticated computer models to calculate their trajectories based on observations.
Could 3I/ATLAS have collided with Jupiter?
While it got relatively close, current data suggests a direct collision was highly unlikely.
Why is studying interstellar comets important?
They provide insights into the composition and dynamics of planetary systems beyond our own.
What are gravitational forces?
It is the force by which a planet or other body draws objects toward its center. The force of gravity keeps all of the planets in orbit around the sun.
Where can I find the latest information on 3I/ATLAS?
Keep an eye on reputable astronomy websites and research publications for updates. You can follow along as astronomers observe and analyze the data provided from the simulations!
So, the dance of 3I/ATLAS around Jupiter serves as a profound reminder: our solar system isn’t a closed-off bubble. It’s part of a grander cosmic tapestry, constantly interacting with the universe beyond. This interstellar comet’s journey and the data we collect from it, offers insight into the dynamics of our solar system and the makeup of other star systems! The mysteries of comets are still unfolding, and 3I/ATLAS has added another layer of intrigue to the story.